Hey there folks! This being my first article on my blog, it’s a mixed feeling of excitement, pleasure and happiness to put up something publicly available to y’all in a way to share with and help tech geeks to somewhere connect the dots for the bigger picture.
Scrolling through my laptop screen, skimming on few mails and a thought in my mind goes like, “what’s gonna be the topic for my first blog post?”. All of a sudden, few voices away at a distance talk about cryptography and hashing. That instant struck my mind and was the moment of exclamation! So let us write about hashing in simple terms to help beginners get an idea and there it goes.
What are hashes?
In cryptography, the data or a message is encrypted using a specific algorithm called a hashing function which renders an output of a specific size. The hash functions convert meaningful information of varying length into alphanumeric values (also known as hash values, digests or hashes) of fixed length. There are various hashing functions/algorithms used and some of them are as follows.
MD5(Message-Digest algorithm)
SHA1(Secure Hashing Algorithm 1)
SHA256
In digital forensics, the hash matching would greatly help to ensure that the original evidence has not been tampered after the evidence has been collected and preserved with access restrictions. The hash value could be considered as a fingerprint derived for every file/folder based on several algorithms such that the integrity of the file/folder/application could be validated.This hash value check could also be used to make sure that any data transmitted by a trustable source is not tampered in transit by any MITM(Man-In-The-Middle) attacks by a malicious attacker. There are some application vendors that provide the precalculated hash values (MD5, SHA1 or SHA256) to help the end users validate the hashes for the applications after the download is complete.
Having said that, hashing can be used to check the file integrity where the hashing provides an encryption to the data at rest (stored data) and in motion (data in transit). It is to be noted that unlike encryption, hashing is an irreversible process. For this purpose, hackers use rainbow tables to match the hashes.
Calculating MD5 hash value of a file:
There are several commands to determine the hash values of files in both Windows and Linux environments. The commands to calculate the file hash value are as follows.
For Windows:From the Windows command prompt, change the working directory to the path where the file is placed. Then enter the command -> “certutil -hashfile <filename> md5”.
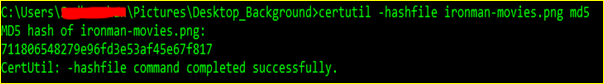
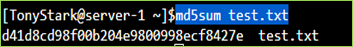
For Linux distributions:From the Linux terminal, simply use the command “md5sum <filename>” to determine the MD5 hash value of a file.
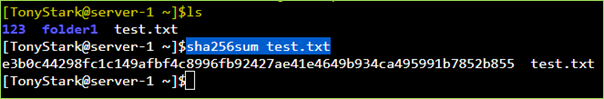
Similarly, in case of a Linux distribution, the SHA256 hash values and hash-checks could be done using the command sha256sum<filename> as follows.
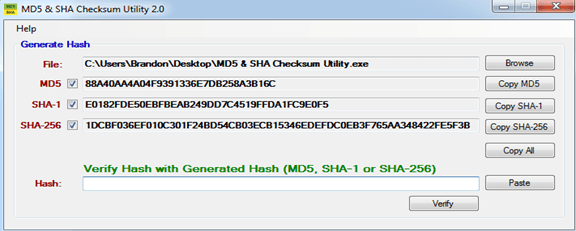
Whereas, for a Windows machine, there are mulitple tools to perform checksum for a particular file to determine hash values and perform hashchecks. One such tool for Windows is “MD5 & SHA Checksum Utility” (Utility Download link: http://raylin.wordpress.com/downloads/md5-sha-1-checksum-utility).
Hence, it is always a security best practice to use strong hashing algorithms to help in securing the data in terms of number of bits of hash key used for encryption. The higher the hashing key bit, the higher the complexity to crack the encryption/hashing.
Thanks for reading!
Very nice notes, keep post more
LikeLike
Thank you “SARAVANAN krishnamurthi”..! 🙂 Do check my latest post on Cloud computing – https://dumpster.tech.blog/2019/12/27/cloud-computing/
LikeLiked by 1 person
Grt one…
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you “Karthick kumar J” 🙂
LikeLike